|
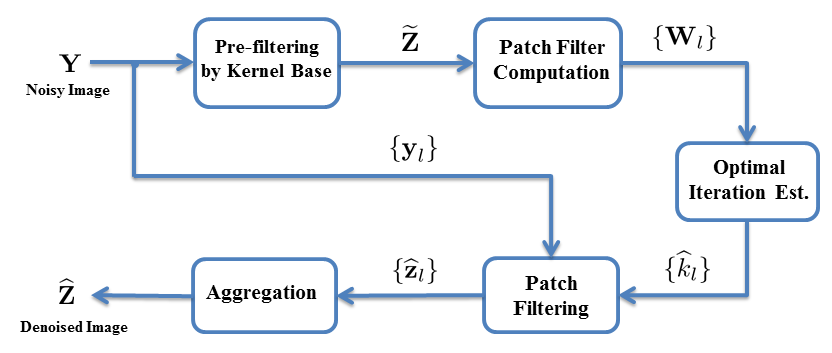
Abstract:Spatial domain image filters (e.g. bilateral filter, NLM, LARK) have achieved great success in denoising. However, their overall performance has not generally surpassed the leading transform domain based filters (such as BM3D). One important reason is that spatial domain filters lack an efficient way to adaptively fine tune their denoising strength; something that is relatively easy to do in transform domain method with shrinkage operators. In the pixel domain, the smoothing strength is usually controlled globally by, for example, tuning a regularization parameter. In this paper, we propose SAIF (Spatially Adaptive Iterative Filtering), a new strategy to control the denoising strength locally for any spatial domain method. This approach is capable of filtering local image content iteratively using the given base filter, while the type of iteration and the iteration number are automatically optimized with respect to estimated risk (i.e. mean-squared error). In exploiting the estimated local SNR, we also present a new risk estimator which is different than the often-employed SURE method and exceeds its performance in many cases. Experiments illustrate that our strategy can significantly relax the base algorithm's sensitivity to its tuning (smoothing) parameters, and effectively boost the performance of several existing denoising filters to generate state-of-the-art results under both simulated and practical conditions. |
Manuscript:H. Talebi, X. Zhu and P. Milanfar, How to SAIF-ly Boost Denoising Performance, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol 22, No. 4, pp. 1470-1485, April 2013. (PDF) |
MATLAB Code:This software is provided for non-commercial research purposes only. Use at your own risk. No warranty is implied by this distribution. Copyright © 2013 by University of California. (Download) |
Examples:
|